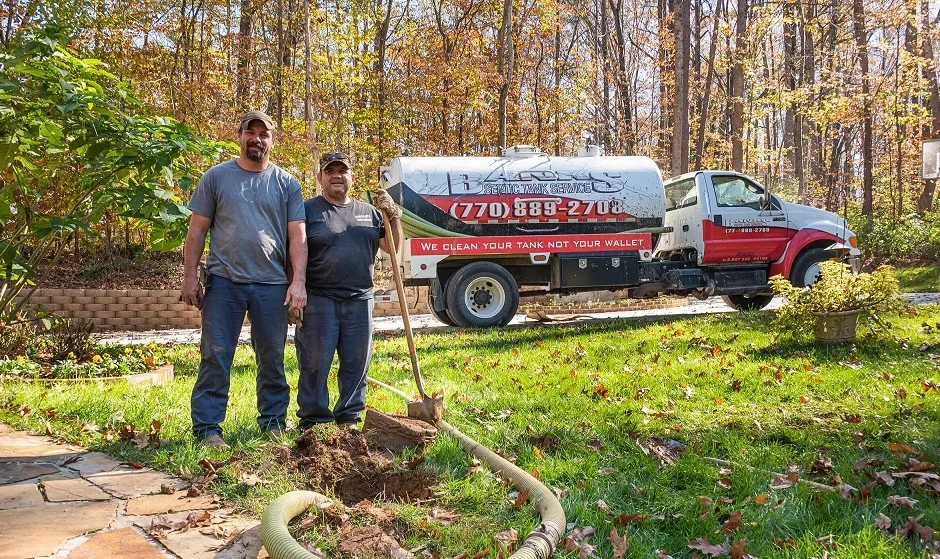
While septic tank pumping is primarily associated with maintaining a functional wastewater treatment system, it also plays a crucial role in preserving and improving soil health. The relationship between septic systems and the soil on your property is symbiotic, with each influencing the other’s well-being. In this article, we will explore the connection between septic tank pumping and soil health, emphasizing the importance of responsible septic system maintenance for both a functional system and thriving soil.
Understanding the Role of Septic Systems
Before delving into the impact on soil health, let’s understand the essential role of septic systems:
- Wastewater Treatment: A septic system is responsible for treating wastewater from your home. It consists of a septic tank that separates solids from liquids and a drain field where effluent is released into the soil for further purification.
- Natural Filtration: The soil in the drain field acts as a natural filter, allowing effluent to percolate through it while removing impurities and contaminants. This process is crucial for ensuring that treated wastewater does not harm the environment.
The Impact of Septic Tank Pumping on Soil Health
Septic tank pumping directly influences soil health in several ways:
- Preventing Soil Saturation: When a septic tank becomes overloaded with solids due to neglect, it can release excessive effluent into the drain field. This overloading can lead to soil saturation, making it less effective at filtering and purifying wastewater.
- Impact: Regular septic tank pumping ensures that effluent entering the drain field is at an appropriate volume, preventing soil saturation and maintaining the soil’s filtration capabilities.
- Minimizing Soil Compaction: Soil compaction can occur if the drain field becomes clogged with solids or if effluent is released too frequently. Compacted soil has reduced pore space, which restricts water infiltration and can lead to drainage issues.
- Impact: Properly maintained septic systems with regular pumping prevent soil compaction, allowing the soil to maintain its natural structure and function.
- Nutrient Distribution: Effluent from septic systems contains essential nutrients like nitrogen and phosphorus. When septic systems are well-maintained, these nutrients can enrich the soil, acting as a natural fertilizer.
- Impact: Healthy soil benefits from the nutrients in effluent, potentially enhancing plant growth and overall soil fertility.
- Avoiding Contamination: Neglected septic systems can release poorly treated effluent, including pathogens and contaminants, into the soil. This contamination can affect soil quality and potentially harm groundwater sources.
- Impact: Routine septic tank pumping ensures that effluent is adequately treated before entering the soil, reducing the risk of soil contamination and protecting water quality.
- Preserving Soil Structure: Soil health relies on a balance of organic matter and microorganisms. When septic systems overload the soil with solids, it can disrupt this balance and negatively impact soil structure.
- Impact: By removing excess solids through septic tank pumping, the soil can maintain its organic matter and microbial diversity, promoting a healthy and fertile environment.
Maintaining a Harmonious Relationship
To ensure a harmonious relationship between septic systems and soil health, consider the following practices:
- Regular Pumping: Follow a recommended septic tank pumping schedule based on your system’s size, household usage, and local regulations. This prevents overloading the soil with solids and protects soil health.
- Water Conservation: Practice water conservation to reduce the strain on your septic system. Conserving water not only benefits your septic system but also minimizes stress on the soil.
- Responsible Product Use: Use septic-safe products, including toilet paper, cleaning agents, and personal care items. These products help maintain the balance of beneficial microorganisms in the soil.
- Proper Drain Field Maintenance: Protect the drain field by avoiding heavy traffic, parking, or construction activities over it. Keep it clear of trees and shrubs with extensive root systems that can disrupt soil structure.
- Regular Soil Testing: Periodically test the soil in and around your drain field to assess its health and detect any signs of contamination or nutrient imbalances.
- Professional Inspections: Schedule professional inspections of your septic system to identify potential issues and ensure it is functioning correctly.
Conclusion
Septic tank pumping and soil health are intricately connected, with each influencing the well-being of the other. Responsible septic system maintenance, including regular pumping, not only ensures the proper functioning of your wastewater treatment system but also promotes thriving soil. By preventing soil saturation, minimizing compaction, distributing essential nutrients, avoiding contamination, and preserving soil structure, you can maintain a harmonious relationship between your septic system and soil health. This symbiotic connection not only benefits your property but also contributes to the overall environmental health of your surroundings.